This is a project in the “Algorithms & Data Structures” course of the ECE department at the University of Patras, for the academic year 2010 - 2011. This was my first-ever (system-level) program. This is where and when I learned C. Sadly that happened in my \(4^{th}\) year of study. But anyways, that’s a story for another time.
The setup for the project is that the government wants to go all digital with the receipts, and so it distributes cards to all citizens to use with their everyday purchases. The data from those purchases are sent and logged in some remote server, and then you are supposed to build a system (involving a hash table) that will satisfy the following requirements:
- What is the number of collisions in the hash table?
- Provide the ability to delete all the records of a card.
- Display the purchase records of a person or a family when you are provided with a number of card IDs dynamically, or all together through a file.
- Display the expenses of a person or a family (in some year) when you are provided with a number of card IDs.
- Which person has purchased the most products/services?
- What is the most desirable product/service for a person or a family?
Next you can see the menu created and a freestyle flow diagram of the main procedures.
Menu:
1. Insert a new file of Purchases
2. Delete cards in the hash table
3. Display the number of collisions
4. Display the load factor in the hash table
5. Display the details of a card ID
6. Search for data about a card or a set of cards
7. Display the cards with the highest usage
8. Settings
9. Exit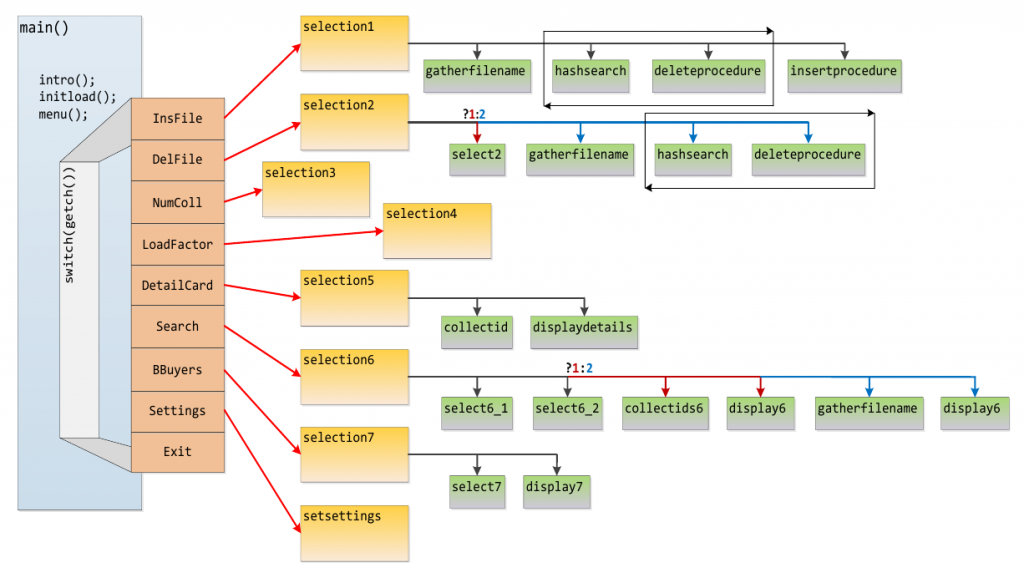
The application is provided with files that have the number of unique card IDs in the first line, and all the purchase records after that. The records have the following format:
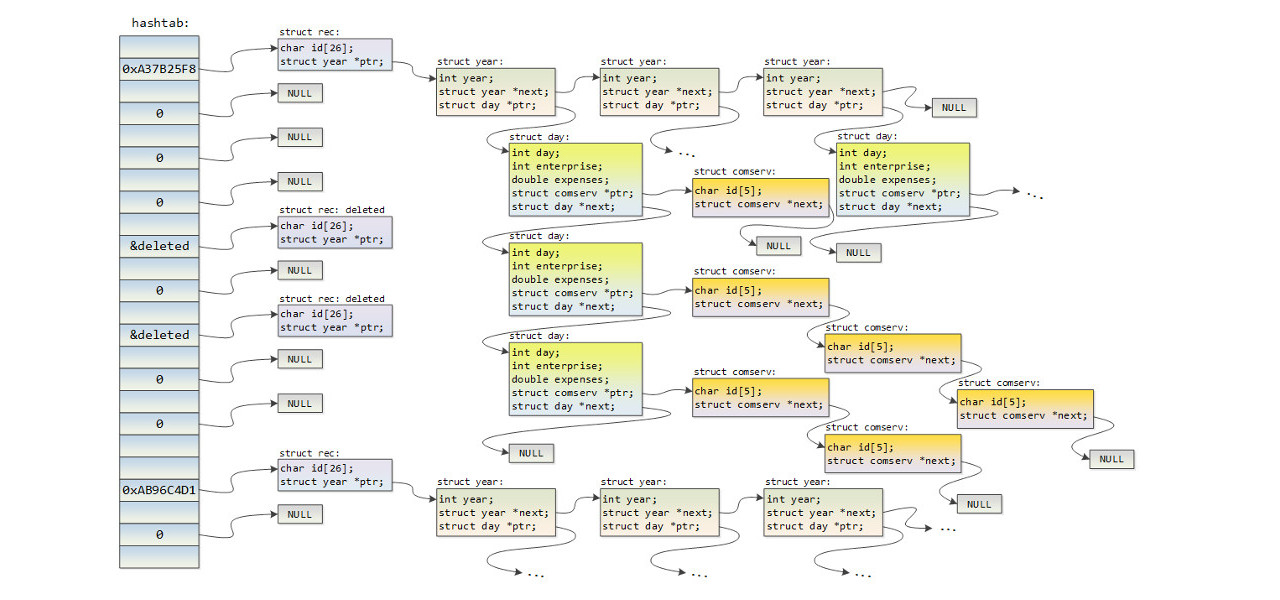
<card-id>;<day-of-year>;<year>;<company-code>;<total-cost>;<list-of-product-codes>Of course, the whole deal with this assignment is how you are gonna arrange the data in memory so that you are able to answer all the questions efficiently. Having defined the data structure, everything else is just a matter of writing some code. The data structure created appears on the following figure.
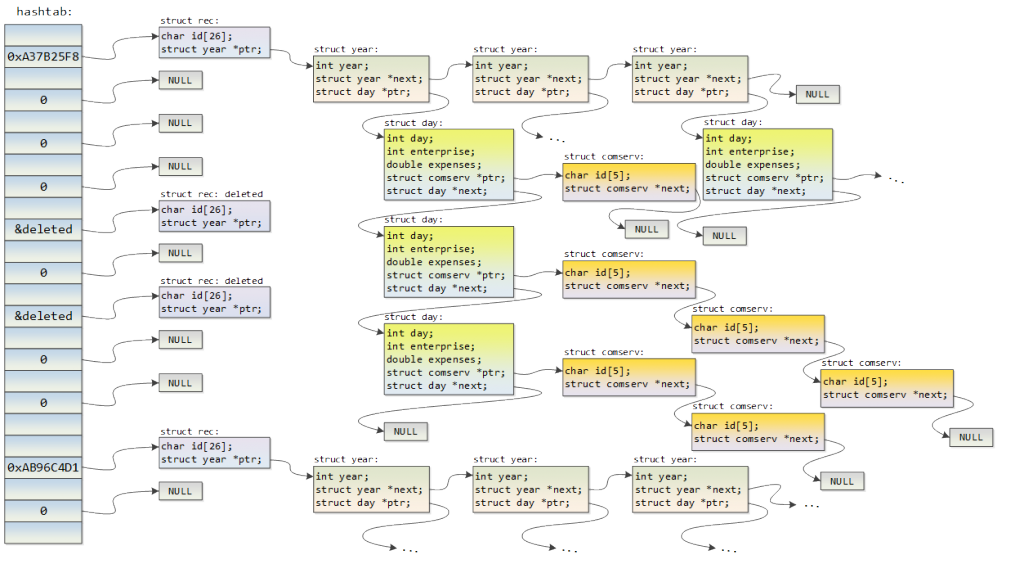
That’s all. The application is able to load 100.000 records in about a second, and get instant results (sample output below).

The source code is available on GitHub.